Usage
You can get started by using the connection flags or by using a configuration file with the connection params.
$ dblab [flags]
or
$ dblab [command]
Available Commands¶
help |
Help about any command |
|---|---|
version |
The version of the project |
Flags¶
dblab is a terminal UI based interactive database client for Postgres, MySQL and SQLite3.
Usage:
dblab [flags]
dblab [command]
Available Commands:
help Help about any command
version The version of the project
Flags:
--cfg-name string Database config name section
--config Get the connection data from a config file (default locations are: current directory, $HOME/.dblab.yaml or $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/.dblab.yaml)
--db string Database name (optional)
--driver string Database driver
--encrypt string [strict|disable|false|true] data sent between client and server is encrypted or not
-h, --help help for dblab
--host string Server host name or IP
--limit uint Size of the result set from the table content query (should be greater than zero, otherwise the app will error out) (default 100)
--pass string Password for user
--port string Server port
--schema string Database schema (postgres only)
--socket string Path to a Unix socket file
--ssh-host string SSH Server Hostname/IP
--ssh-key string File with private key for SSH authentication
--ssh-key-pass string Supports connections with protected private keys with passphrase
--ssh-pass string SSH Password (Empty string for no password)
--ssh-port string SSH Port
--ssh-user string SSH User
--ssl string SSL mode
--ssl-verify string [enable|disable] or [true|false] enable ssl verify for the server
--sslcert string This parameter specifies the file name of the client SSL certificate, replacing the default ~/.postgresql/postgresql.crt
--sslkey string This parameter specifies the location for the secret key used for the client certificate. It can either specify a file name that will be used instead of the default ~/.postgresql/postgresql.key, or it can specify a key obtained from an external “engine”
--sslpassword string This parameter specifies the password for the secret key specified in sslkey
--sslrootcert string This parameter specifies the name of a file containing SSL certificate authority (CA) certificate(s) The default is ~/.postgresql/root.crt
--timeout string in seconds (default is 0 for no timeout), set to 0 for no timeout. Recommended to set to 0 and use context to manage query and connection timeouts
--trace-file string File name for trace log
--trust-server-certificate string [false|true] server certificate is checked or not
-u, --url string Database connection string
--user string Database user
-v, --version version for dblab
--wallet string Path for auto-login oracle wallet
Use "dblab [command] --help" for more information about a command.
Navigation¶
If the query panel is active, type the desired query and press Ctrl+Space to see the results on the rows panel below. Otherwise, you might me located at the tables panel, then you can navigate by using the arrows Up and Down (or the keys k and j respectively).
If you want to see the rows of a table, press Enter.
To see the schema of a table, locate yourself on the rows panel and press Ctrl+S to switch to the structure panel, then switch Ctrl+S to switch back.
The same can be achieved for the constraints view by pressing Ctrl+F to go back and forth between the rows and the constraints panels.
Now, there's a menu to navigate between hidden views by just clicking on the desired options:
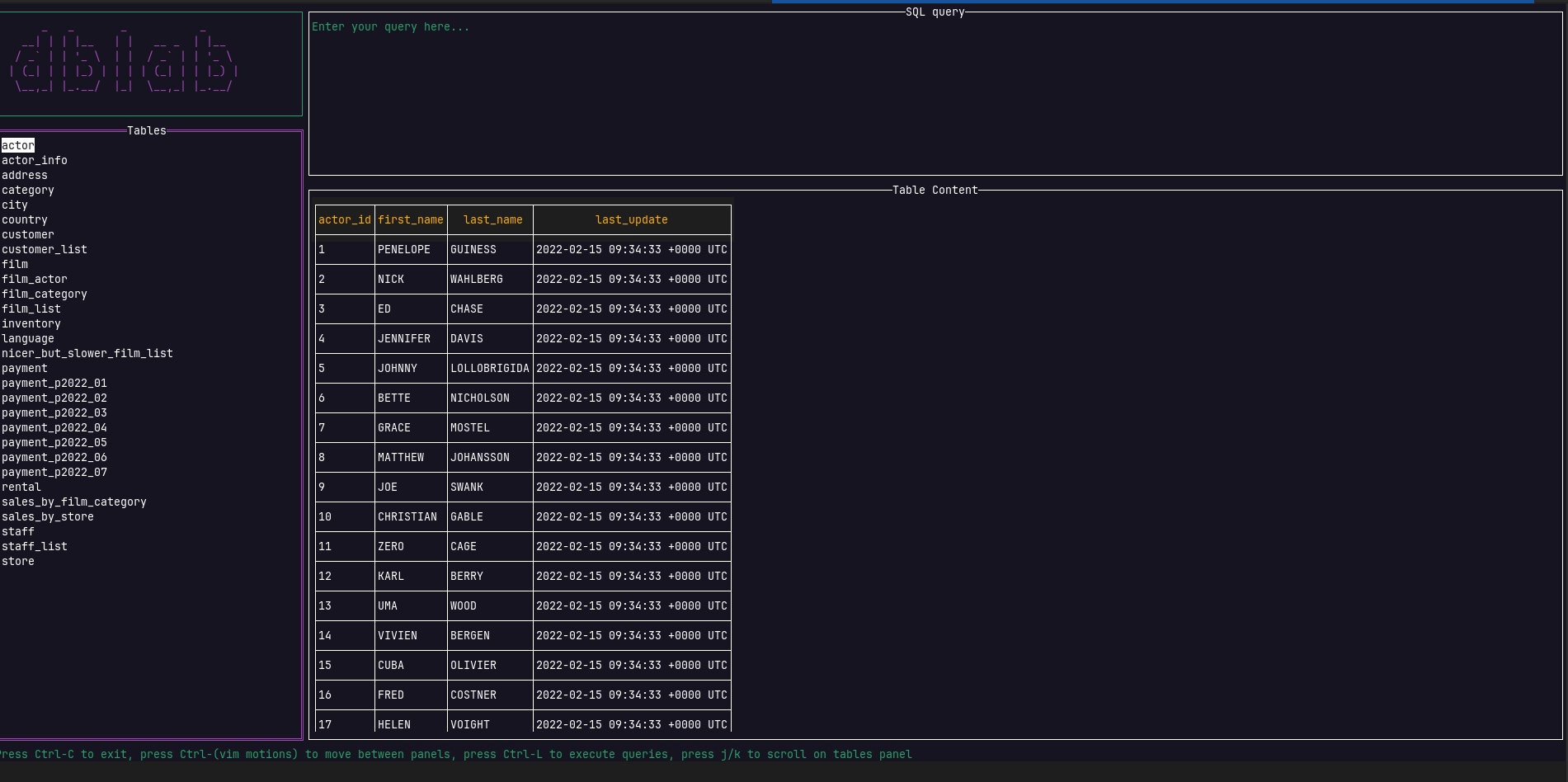
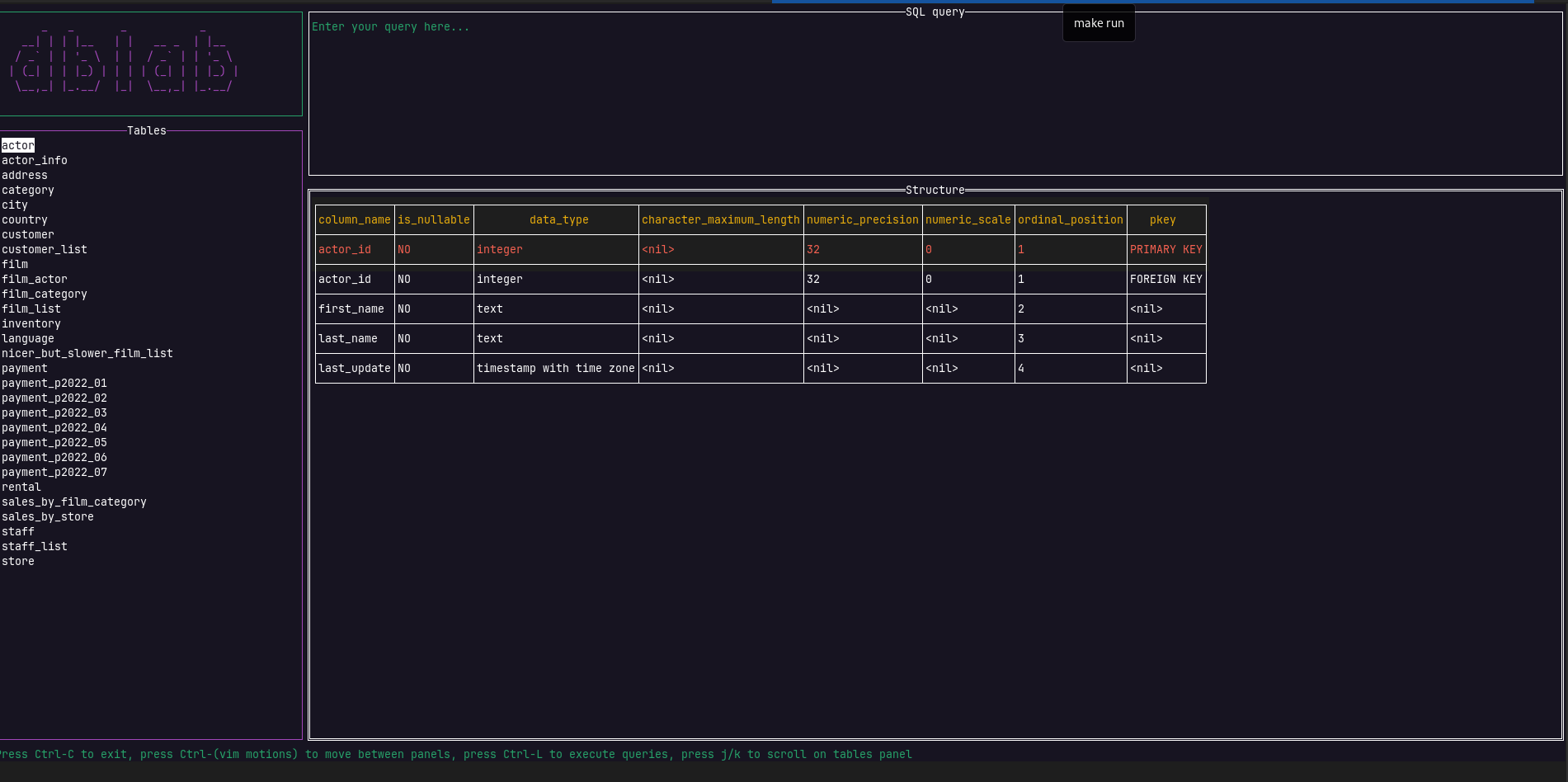
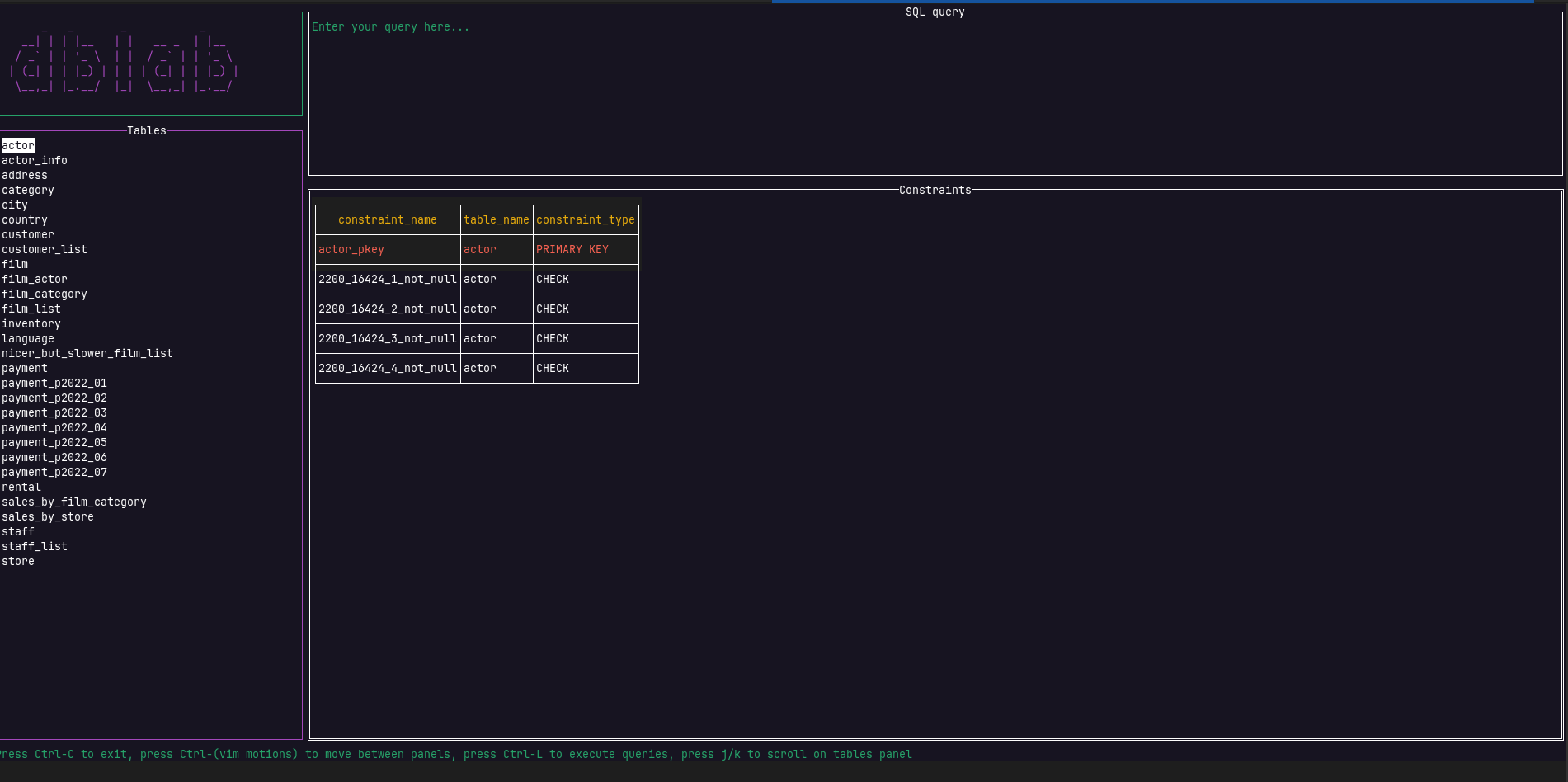
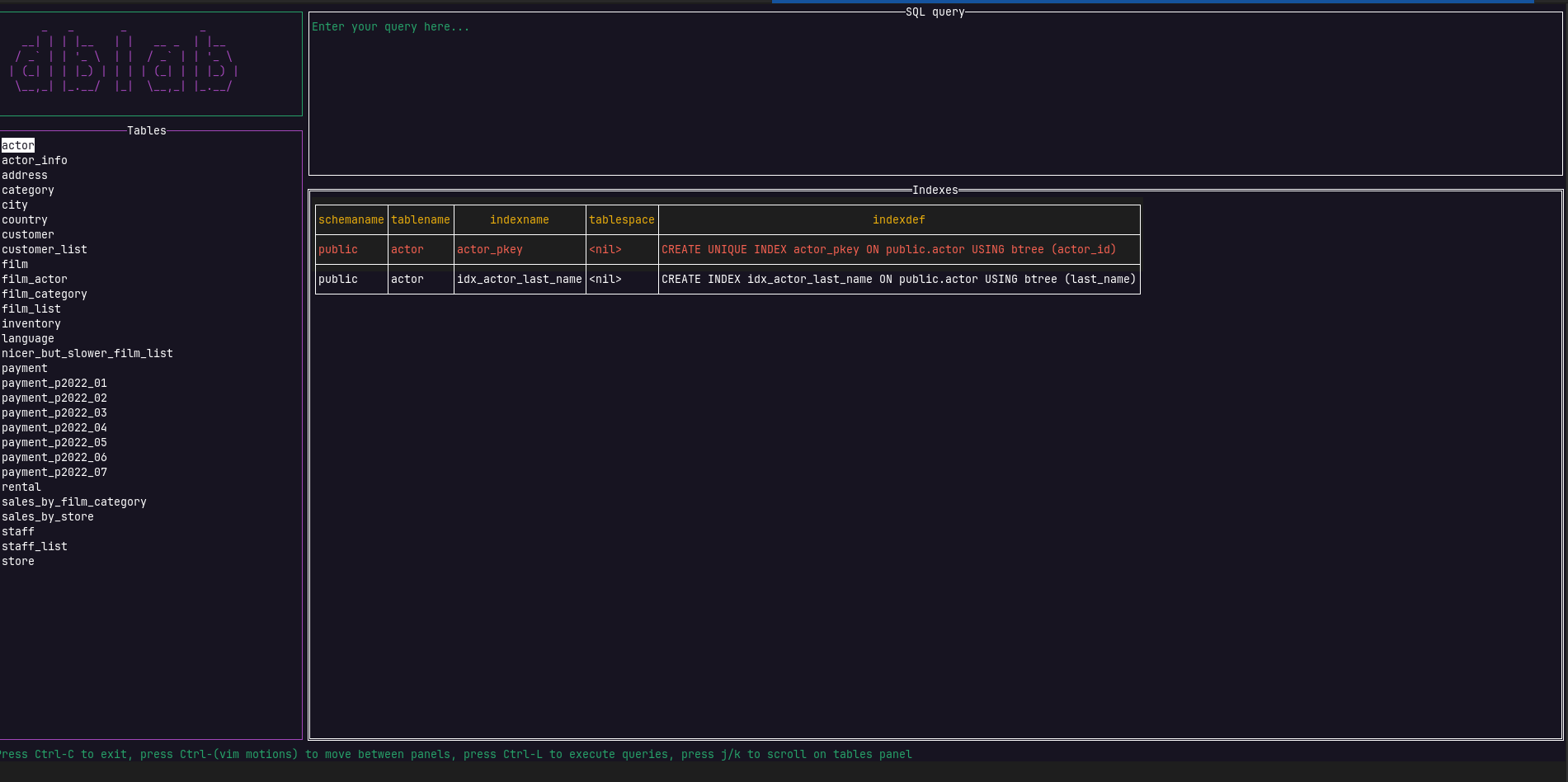
As you may have noticed, navigation has already been added, so every time you query the content of a listed table, the result set is going to be paginated. This allows to the user dealing with large tables, optimizing resources.
Just hit the BACK and NEXT buttons to go back and forth.
Key Bindings¶
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| Ctrl+Space | If the query panel is active, execute the query |
| Ctrl+D | Cleans the whole text from the query editor, when the editor is selected |
| Enter | If the tables panel is active, list all the rows as a result set on the rows panel and display the structure of the table on the structure panel |
| Ctrl+S | If the rows panel is active, switch to the schema panel. The opposite is true |
| Ctrl+F | If the rows panel is active, switch to the constraints view. The opposite is true |
| Ctrl+I | If the rows panel is active, switch to the indexes view. The opposite is true |
| Ctrl+H | Toggle to the panel on the left |
| Ctrl+J | Toggle to the panel below |
| Ctrl+K | Toggle to the panel above |
| Ctrl+L | Toggle to the panel on the right |
| Arrow Up | Next row of the result set on the panel. Views: rows, table, constraints, structure and indexes |
| k | Next row of the result set on the panel. Views: rows, table, constraints, structure and indexes |
| Arrow Down | Previous row of the result set on the panel. Views: rows, table, constraints, structure and indexes |
| j | Previous row of the result set on the panel. Views: rows, table, constraints, structure and indexes |
| Arrow Right | Horizontal scrolling on the panel. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| l | Horizontal scrolling on the panel. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| Arrow Left | Horizontal scrolling on the panel. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| h | Horizontal scrolling on the panel. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| h | Horizontal scrolling on the panel. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| g | Move cursor to the top of the panel's dataset. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| G | Move cursor to the bottom of the panel's dataset. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| Ctrl-F | Move down by one page. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| Ctrl-B | Move up by one page. Views: rows, constraints, structure and indexes |
| Ctrl+c | Quit |
Connection Examples¶
You can start the app without passing flags or parameters, so then an interactive command prompt will ask for the connection details.
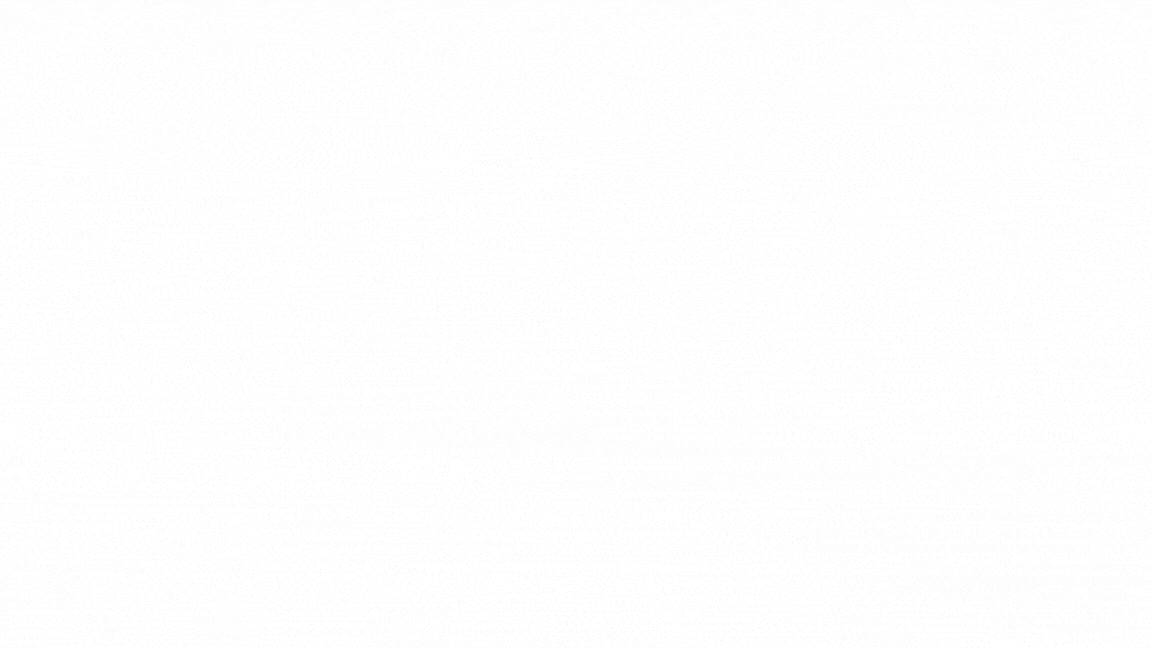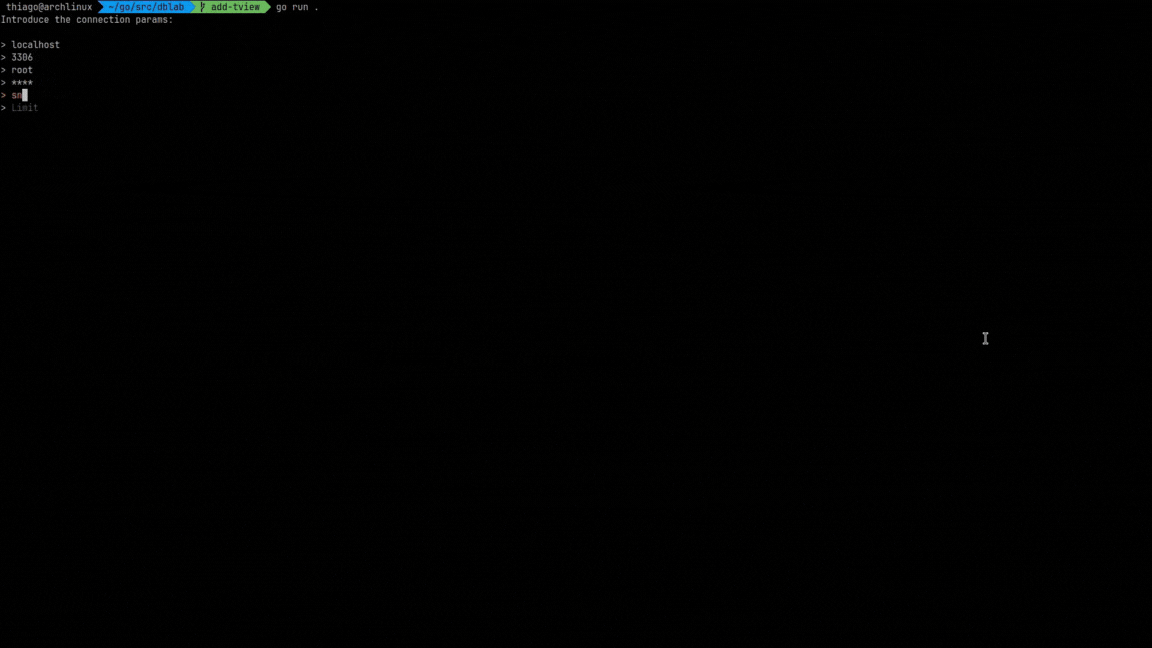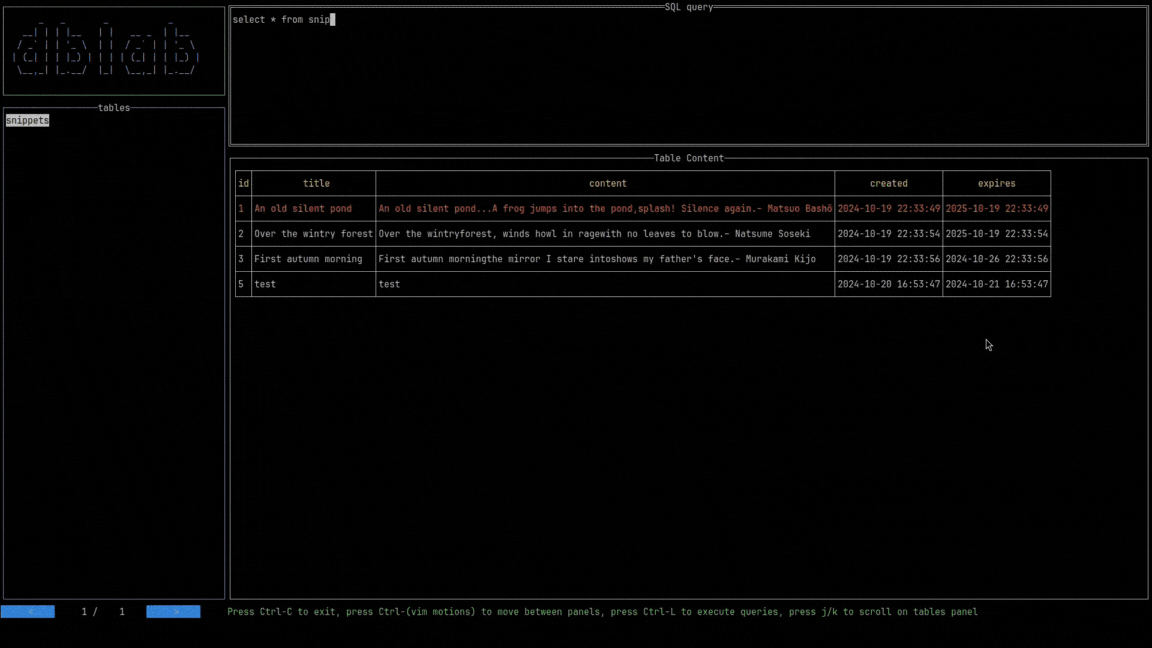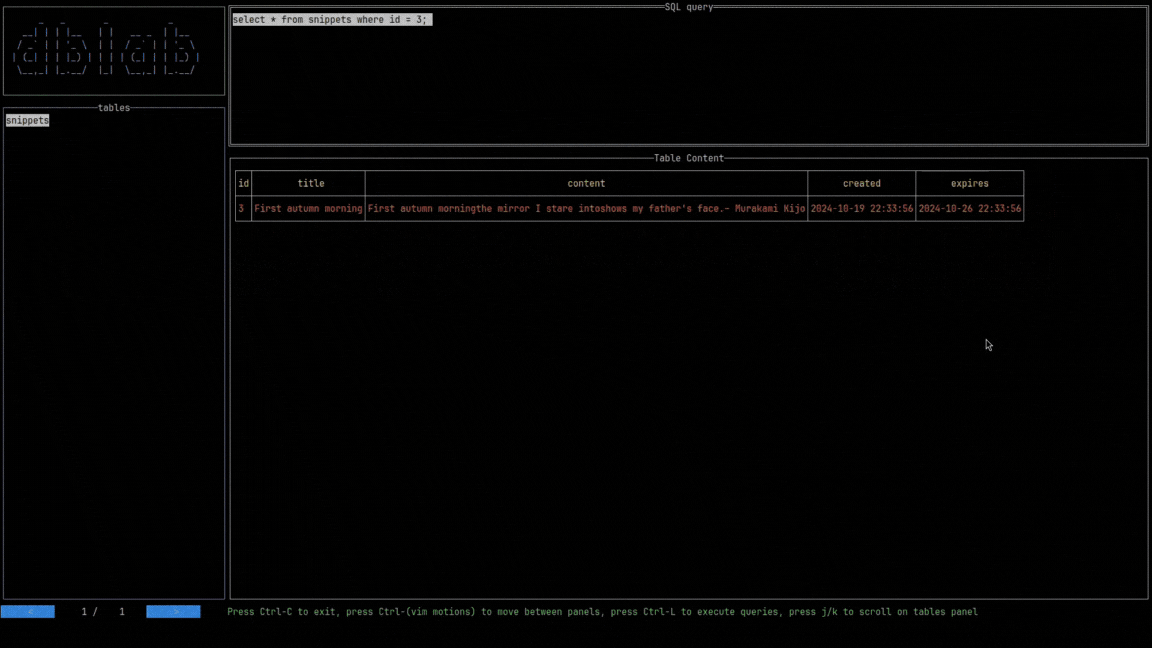
Otherwise, you can explicitly include the connection details using multiple parameters:
dblab --host localhost --user myuser --db users --pass password --ssl disable --port 5432 --driver postgres --limit 50
dblab --db path/to/file.sqlite3 --driver sqlite
dblab --host localhost --user system --db FREEPDB1 --pass password --port 1521 --driver oracle --limit 50
dblab --host localhost --user SA --db msdb --pass '5@klkbN#ABC' --port 1433 --driver sqlserver --limit 50
Connection URL scheme is also supported:
dblab --url postgres://user:password@host:port/database?sslmode=[mode]
dblab --url mysql://user:password@tcp(host:port)/db
dblab --url file:test.db?cache=shared&mode=memory
dblab --url 'oracle://user:password@localhost:1521/db'
dblab --url 'sqlserver://SA:myStrong(!)Password@localhost:1433?database=tempdb&encrypt=true&trustservercertificate=false&connection+timeout=30'
if you're using PostgreSQL, you have the option to define the schema you want to work with, the default value is public.
dblab --host localhost --user myuser --db users --pass password --schema myschema --ssl disable --port 5432 --driver postgres --limit 50
dblab --url postgres://user:password@host:port/database?sslmode=[mode] --schema myschema
As a request made in #125, support for MySQL/MariaDB sockets was integrated.
dblab --url "mysql://user:password@unix(/path/to/socket/mysql.sock)/dbname?charset=utf8"
dblab --socket /path/to/socket/mysql.sock --user user --db dbname --pass password --ssl disable --port 5432 --driver mysql --limit 50
Postgres connection through Unix sockets:
$ dblab --url "postgres://user:password@/dbname?host=/path/to/socket"
$ dblab --socket /path/to/socket --user user --db dbname --pass password --ssl disable --port 5432 --driver postgres --limit 50
Now, it is possible to ensure SSL connections with PostgreSQL databases. SSL related parameters has been added, such as --sslcert, --sslkey, --sslpassword, --sslrootcert. More information on how to use such connection flags can be found here.
dblab --host db-postgresql-nyc3-56456-do-user-foo-0.fake.db.ondigitalocean.com --user myuser --db users --pass password --schema myschema --port 5432 --driver postgres --limit 50 --ssl require --sslrootcert ~/Downloads/foo.crt
SSH Tunnel¶
Now, it's possible to connect to Postgres or MySQL (more to come later) databases on a server via SSH using password or a ssh key files.
To do so, 6 new flags has been added to the dblab command:
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
| --ssh-host | SSH Server Hostname/IP |
| --ssh-port | SSH Port |
| --ssh-user | SSH User |
| --ssh-pass | SSH Password (Empty string for no password) |
| --ssh-key | File with private key for SSH authentication |
| --ssh-key-pass | Passphrase for protected private key files |
Examples¶
Postgres connection via ssh tunnel using password:
dblab --host localhost --user postgres --pass password --schema public --ssl disable --port 5432 --driver postgres --limit 50 --ssh-host example.com --ssh-port 22 --ssh-user root --ssh-pass root
Postgres connection via ssh tunnel using ssh private key file:
dblab --host localhost --user postgres --pass password --schema public --ssl disable --port 5432 --driver postgres --limit 50 --ssh-host example.com --ssh-port 22 --ssh-user root --ssh-key my_ssh_key --ssh-key-pass password
Postgres connection using the url parameter via ssh tunnel using password:
dblab --url postgres://postgres:password@localhost:5432/users?sslmode=disable --schema public --ssh-host example.com --ssh-port 22 --ssh-user root --ssh-pass root
MySQL connection via ssh tunnel using password:
dblab --host localhost --user myuser --db mydb --pass 5@klkbN#ABC --ssl enable --port 3306 --driver mysql --limit 50 --ssh-host example.com --ssh-port 22 --ssh-user root --ssh-pass root
MySQL connection via ssh tunnel using ssh private key file:
dblab --host localhost --user postgres --pass password --ssl enable --port 3306 --driver mysql --limit 50 --ssh-host example.com --ssh-port 22 --ssh-user root --ssh-key my_ssh_key --ssh-key-pass passphrase
MySQL connection using the url parameter via ssh tunnel using password:
dblab --url "mysql://myuser:5@klkbN#ABC@mysql+tcp(localhost:3306)/mydb" --driver mysql --ssh-host example.com --ssh-port 22 --ssh-user root --ssh-pass root
Configuration¶
Entering the parameters and flags every time you want to use it is tedious,
so dblab provides a couple of flags to help with it: --config and --cfg-name.
dblab is going to look for a file called .dblab.yaml. Currently, there are three places where you can drop a config file:
- $XDG_CONFIG_HOME ($XDG_CONFIG_HOME/.dblab.yaml)
- $HOME ($HOME/.dblab.yaml)
- . (the current directory where you run the command line tool)
If you want to use this feature, --config is mandatory and --cfg-name may be omitted. The config file can store one or multiple database connection sections under the database field. database is an array, previously was an object only able to store a single connection section at a time.
We strongly encourage you to adopt the new format as of v0.18.0. --cfg-name takes the name of the desired database section to connect with. It can be omitted and its default values will be the first item on the array.
As of v0.21.0, ssl connections options are supported in the config file.
dbladb --config
dblab --config --cfg-name "prod"
Key bindings configuration¶
Key bindings can be configured through the .dblab.yaml file. There is a field called keybindings where key bindings can be modified. See the example to see the full list of the key bindings subject to change. The file shows the default values. The list of the available key bindings belongs to the tcell library. Specifically, see the KeyNames map, for an accurate reference.
.dblab.yaml example¶
database:
- name: "test"
host: "localhost"
port: 5432
db: "users"
password: "password"
user: "postgres"
driver: "postgres"
# optional
# postgres only
# default value: public
schema: "myschema"
- name: "prod"
# example endpoint
host: "mydb.123456789012.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com"
port: 5432
db: "users"
password: "password"
user: "postgres"
schema: "public"
driver: "postgres"
ssl: "require"
sslrootcert: "~/.postgresql/root.crt."
- name: "oracle"
host: "localhost"
port: 1521
db: "FREEPDB1 "
password: "password"
user: "system"
driver: "oracle"
ssl: "enable"
wallet: "path/to/wallet"
ssl-verify: true
- name: "sqlserver"
driver: "sqlserver"
host: "localhost"
port: 1433
db: "msdb"
password: "5@klkbN#ABC"
user: "SA"
- name: "ssh-tunnel"
host: "localhost"
port: 5432
db: "users"
password: "password"
user: "postgres"
schema: "public"
driver: "postgres"
ssh-host: "example.com"
ssh-port: 22
ssh-user: "ssh-user"
ssh-pass: "password"
# should be greater than 0, otherwise the app will error out
limit: 50
keybindings:
run-query: 'Ctrl-Space'
structure: 'Ctrl-S'
indexes: 'Ctrl-I'
constraints: 'Ctrl-T'
clear-editor: 'Ctrl-D'
navigation:
up: 'Ctrl-K'
down: 'Ctrl-J'
left: 'Ctrl-H'
right: 'Ctrl-L'
Or for sqlite:
database:
- name: "prod"
db: "path/to/file.sqlite3"
driver: "sqlite"
only the host and ssl fields are optionals. 127.0.0.1 and disable, respectively.